Schemas
When Governor has observed an object in the cloud, it tries to classify it.
This is done for two reasons.
First, it depends on the object class whether you can invoke an action. For example, you cannot reset the password of a Guest user, but you can for a Cloud-only User.
Second, depending on the object class, some configuration properties are kind of "given", you cannot change them. If you would do, you would either break the object or change the entire object "class".
Schema is the classification definition of an Object. Governor use Schemas to classify the observed objects.
There are Basic Schemas pre-defined in Governor, but we can create our own Schemas for more granular classification. This is a powerful tool we can use when our environment needs more complex classification.
For example we could create a Schema to classify users with specific criteria.
ie: [Enforce] Department == "Sales"
Schema Assignment
Schemas are evaluated by Governor when an object has been observed.
When handling an observation result, Governor will request all available information from the inventory and will then try to find the best matching schema for that object.
If the object fulfills all policies of a certain schema, the schema is considered a candidate schema.
The schema with most policy matches wins and is assigned to the object.
Schema Policies
The classification rules for objects are described as Schema Policies.
Each Schema can contain any number of policies to describe the configuration pattern for an object.
When Governor is evaluating schemas, each policy is matched against the object. If a policy is not matched by an object, the corresponding schema does not fit for the object.
Sample
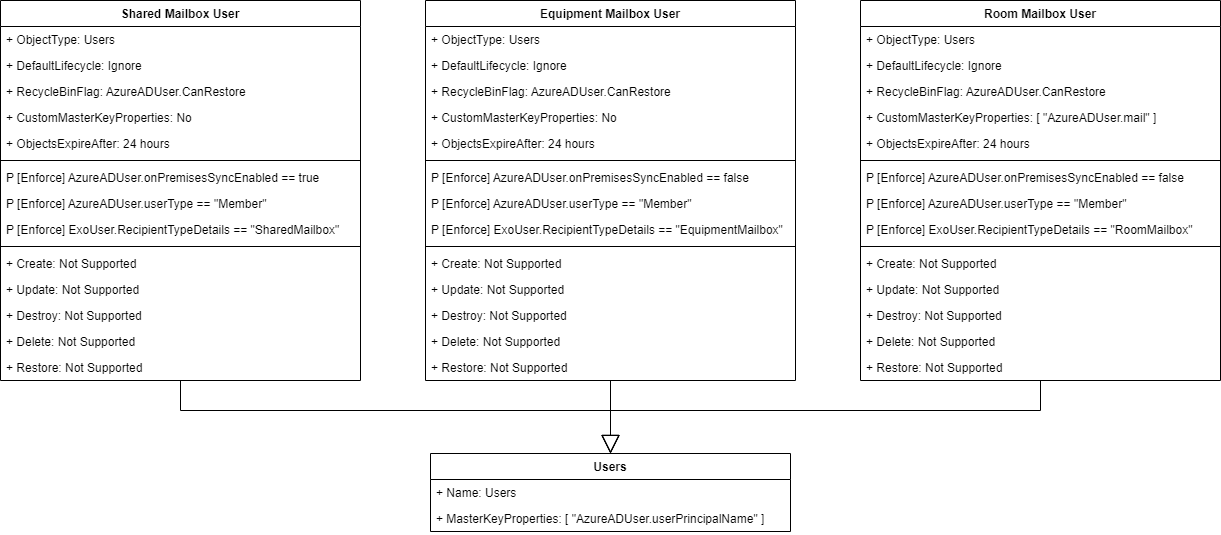
Guest User in Azure AD always have:
- AzureADUser.userType = "Guest"
- AzureADUser.onPremisesSyncEnabled = false
Hybrid User in Azure AD always have:
- AzureADUser.userType = "Member"
- AzureADUser.onPremisesSyncEnabled = true
Cloud-only User in Azure AD always have:
- AzureADUser.userType = "Member"
- AzureADUser.onPremisesSyncEnabled = true
Mail-Enabled Users in Azure AD always have:
- AzureADUser.userType = "Member"
- AzureADUser.onPremisesSyncEnabled = true
- ExoUser.RecipientType = "UserMailbox"
Schema Actions
As soon as an object is classified, we know which actions are supported for that object.
An important feature of the engine is, that you can extend the list of actions (=Powershell scripts) available for an object.
Sample
Guest User in Azure AD:
- Cannot be created, instead you must Invite them.
- Cannot reset password on Guest Users (the password is mangaged in the source domain)
- Cannot have a mailbox (the email address is pointing to the source domain)
Hybrid User in Azure AD:
- Cannot create, instead you must Sync them from local AD to the cloud.
- Cannot reset password (the password is promoted from the local AD to the cloud)
- Cannot move to recycle bin / restore from recycle bin
- Cannot touch most of the properties. They are read-only.
Cloud-only User in Azure AD:
- Can create
- Can reset password
- Can recycle / restore from recycle bin
- Can touch almost all properties
Azure AD User Schemas
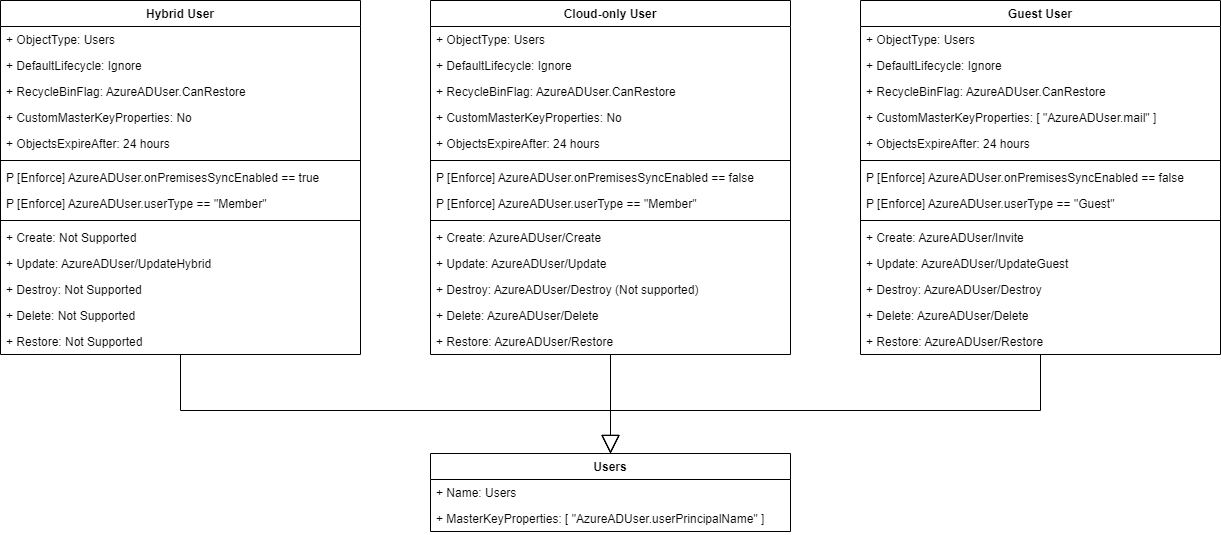
Mailboxes Schemas