Installation
Overview
Cloud Governor is designed to run in an Azure Tenant. As it is based on a microservice architecture, it uses Azure AKS as the compute resource to provide you with the benefits of Kubernetes as the main container orchestrator. For data storage we recommend to use a Azure Database for Postgres to leverage the full power of Azures Cloud services.
To simplify the installation process we decided to use Terraform as Infrastructure as Code to provide a transparent and reliable installation/provisioning that can be customized to any environment and customer need. In addition it reduces the manual effort to a minimum and can be scaled upon multiple environments.
Find the technical architecture here
Prerequesites for Governor
Users and Permissions
To be able to provision all the needed services it is necessary to create a Service Principal that is capable to perform the installation and has all the needed permissions to do so. This ensures that all the changes are transparent in your Tenant and you have full control about the application.
The following Role assignments need to be assigned to the Terraform user/Service Principal.
158c047a-c907-4556-b7ef-446551a6b5f7 Cloud Application Administrator
e8611ab8-c189-46e8-94e1-60213ab1f814 Privileged Role Administrator
Once the Service Principal is created and has the nessecary roles assigned to it, you need to create a secret to authenticate with the above user.
DNS and networking
The Terraform provisioning will automatically create a DNS zone to register all needed URL`s (CNAMES, A Records) in your environment. As DNS is usually already managed within your company, it is necessary to create a link to the newly created zone to make DNS work properly.
The created DNS zone will handle everything else:
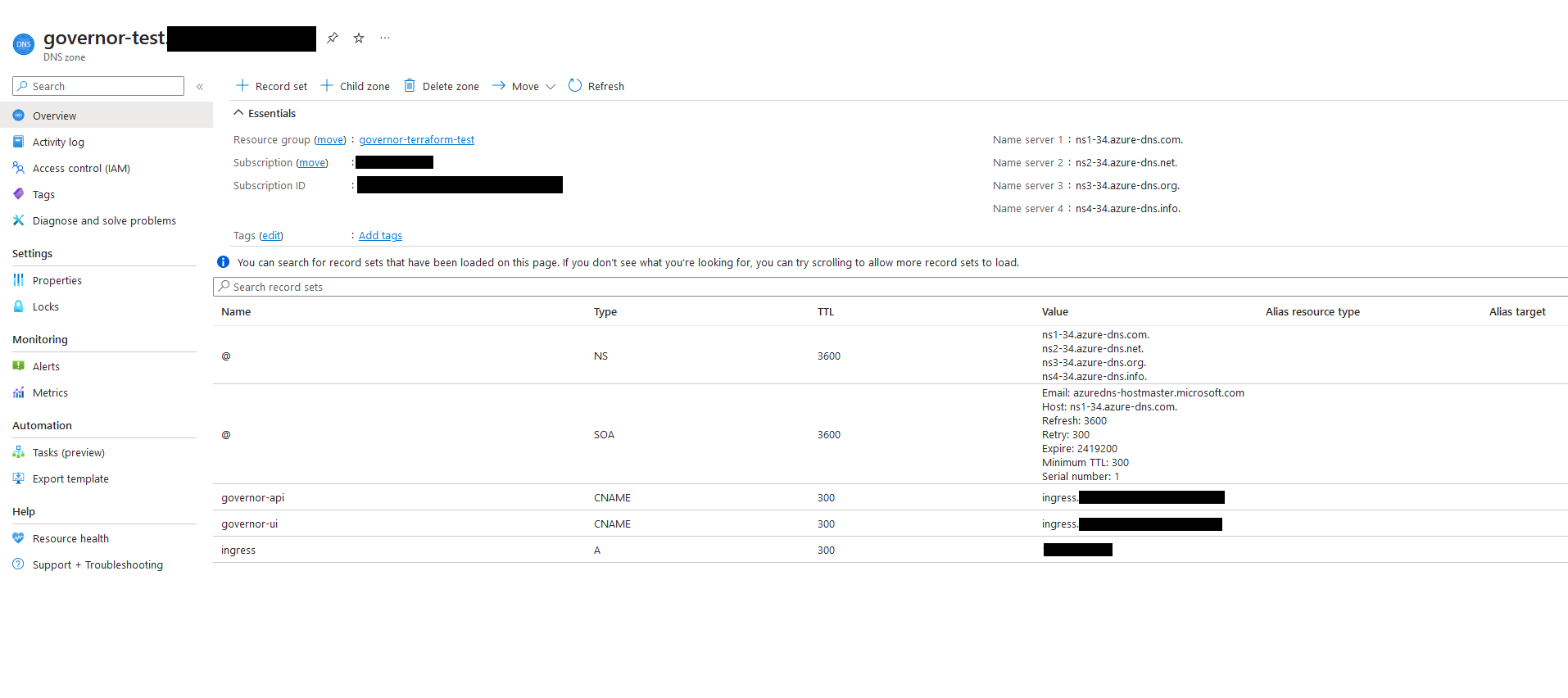
A public IP Address will be automatically created and linked to the DNS Zone. If you choose to use internal IP Addresses, FQDN Namespaces and certificates, please get in contact with us and we will provide you with a different module/solution.
Use Terraform modules to provision Governor
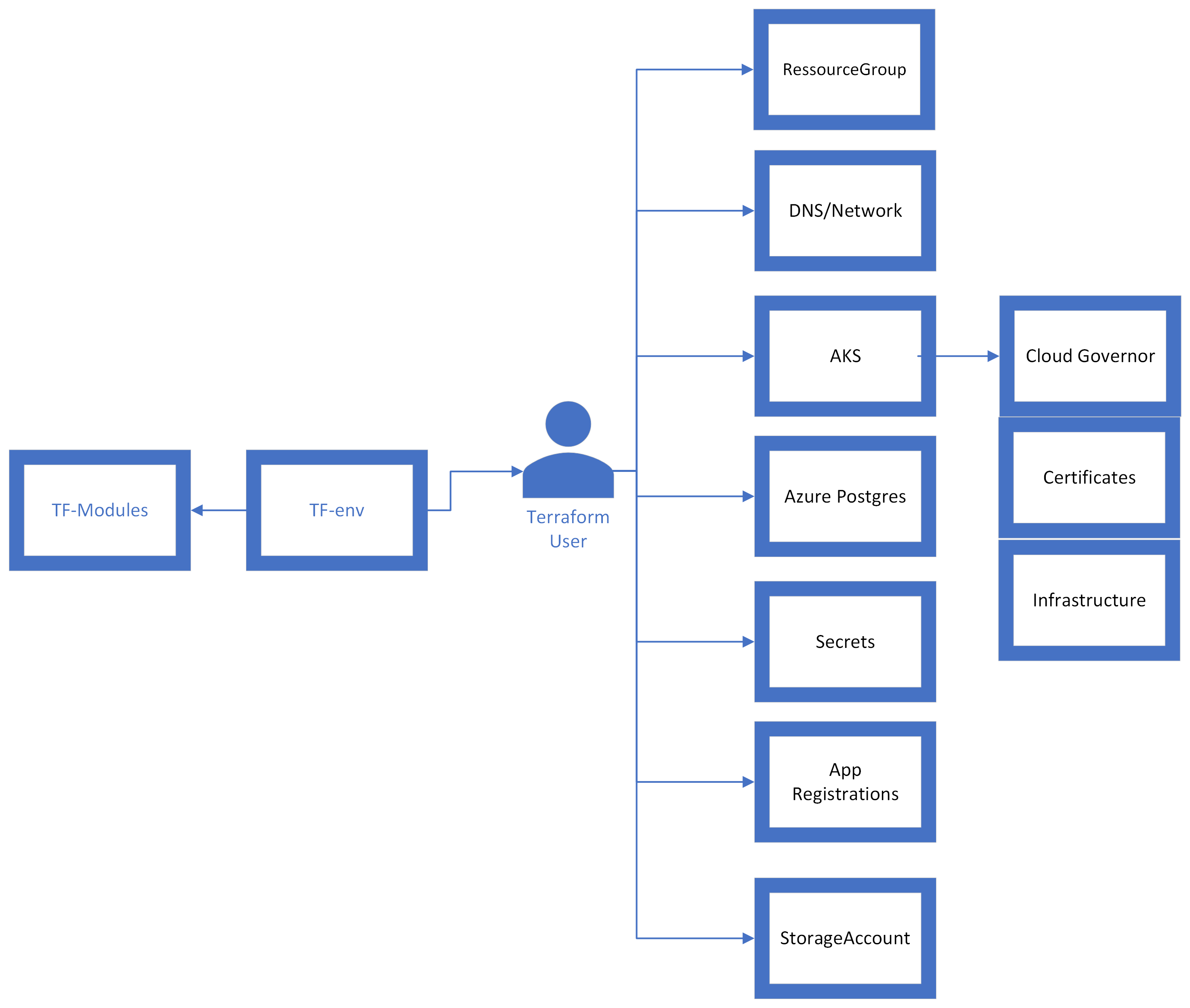
Databoat will provide access to Governor's Terraform Modules git repository that handles all the needed elements in Azure. As our modules are evolving, we run version control them centrally to ensure a high level of quality and reliability.
With the authenticated Terraform Service Principal it will create everything you need to run governor such as:
├── azure-aks
├── azure-app-registration
├── azure-network
├── azure-postgresql
├── azure-resourcegroup
├── azure-secrets
├── azure-secrets-getter
├── azure-storage-account
├── kubernetes-governor
├── kubernetes-infra
This ensures an easy and secure installation with all needed elements to run Governor "out of the box".
Storage account for Terraform statefile
Terraform knows about the status of your application and stores in a so called "statefile". To store this file in a secure manner you have to create a storage account and a blob storage to store it. You can use the following script to do so:
#!/bin/bash
RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME=tfstate
STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME=tfstate$RANDOM
CONTAINER_NAME=tfstate
# Create resource group
az group create --name $RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME --location "Switzerland North"
# Create storage account
az storage account create --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME --name $STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME --sku Standard_LRS --encryption-services blob
# Create blob container
az storage container create --name $CONTAINER_NAME --account-name $STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME
We will need the storage account later when we configure your actual environment. EACH environment MUST have a separate state file.
Create your environment with the modules
Environment
As described above, Databoat provides Terraform modules to handle the Infrastracture. To use this modules you need to describe a target environment with your individual needs on how to use the modules. Databoat provides a environment template that comes preconfigured and needs to be amended to reflect your needs. The location shall be a git repository to ensure the IaaC approach and track changes automatically and transparent.
The main files that need your attention are:
provider.tf # defines the provider versions and the backend, where the statefile is stored
backend.conf # defines the Tenant and the Terraform users client_id/secret
azure-modules.tf # defines which modules are used to provision the infrastructure
governor.tf # defines the Governor specific variables such as env name, version, location, etc.
policy_db-init-data.sql # defines the initial users that need to be permitted to use Governor
Databoat is happy to help you to define your initial environment. After these steps have been taken, the environment can be installed automatically.
Basic Concepts of Terraform
Once your enviroment description is ready, you can apply the description to your tenant. No additional/manual steps are needed to perform the provisioning and/or updates on an existing environment.
In case of a change in the target environment, such as a Software version upgrade, all you need to do is change the enviroment declaration and Terraform will upgrade the environment and the state it is in. The state only changes if a change has been made to the environment. (Version upgrade, scaling, storage changes, etc.)

Install/Update Enviroment
Initialize Terraform and install governor
-
Install Terraform dependend to your local environment or automated pipeline.
-
Navigate to the terraform environment you created in the prerequesites
cd environments/$YOURENVIRONMENT # change to the actual environment folder
- Authenticate with the governor terraform user
# set client secret for terraform service principal, this is the user that performs all actions within the environment
export TF_VAR_client_secret_service_principal="MAKE-SURE-YOU-HAVE-THE-SECRET"
# initialize the backend configuration
cat backend.conf| envsubst > backend.conf_with_client_secret
terraform init --backend-config=backend.conf_with_client_secret # one-time, at environment folder
# terraform will now download all the declared modules and update the backend
- Plan the installation
Run terraform plan to see what will change.
terraform plan # this pulls the statefile and compares it with the actual description of the environment
- Apply the installation
# to perform an actual change you need to run
terraform apply
Post installation
Grant App Registration permissions (api permissions)
After the successful first installation, an administrator needs to grant the needed admin consent for Governor to make it work properly. Each of the below microservices have different permissions to provide a maximum level of security.
Please grant the needed permissions to:
governor-ui
governor-api
governor-executor
governor-observer
As an example, the observer needs this permissions to do its job:
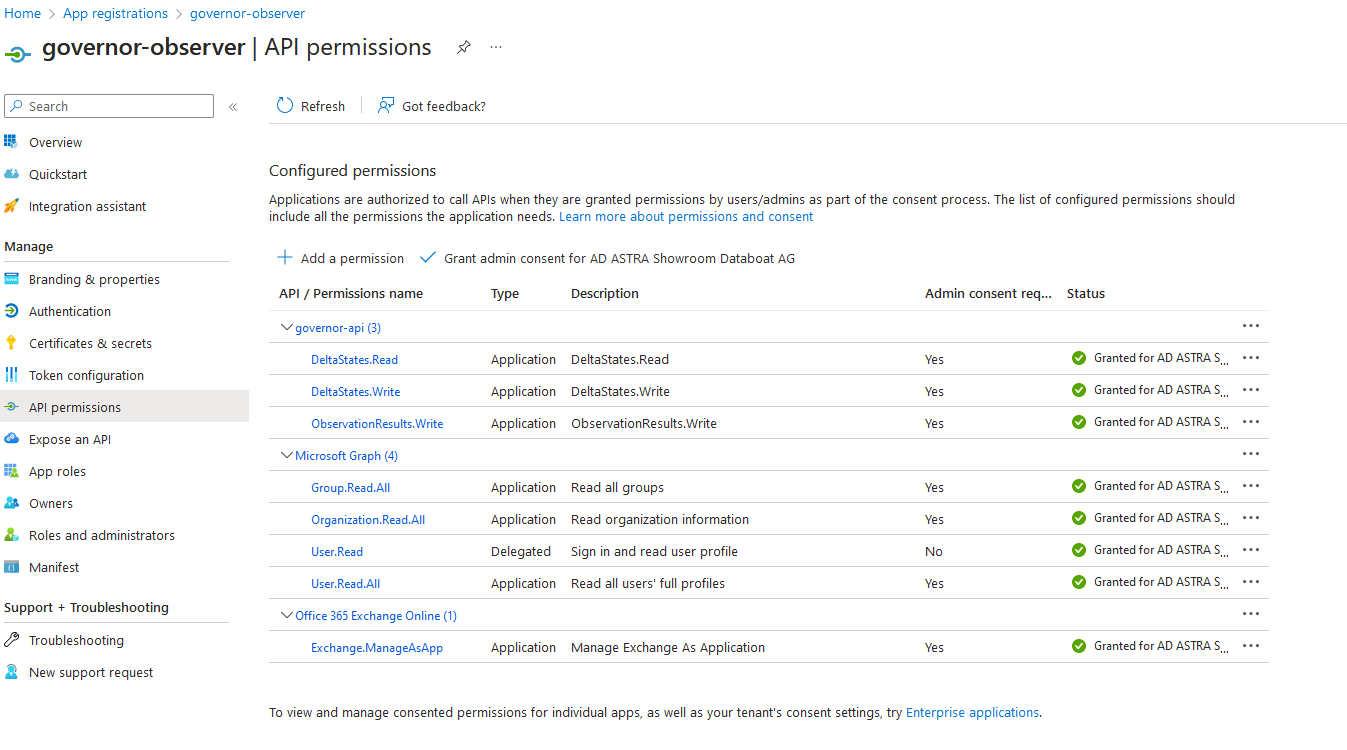
Grant Access to Users to the Governor Api (user permissions)
After the successful first installation, an administrator needs to grant access to specific (human) users to allow them to interact with Governor. This is done in the Enterprise Application governor-api.

Be aware that users must be known to governor api as well, they need to be imported to the policy database. To automate this process you can declare the users within the Terraform environments file (provided with the databoat environment template) :
policy_db-init-data.sql
This ensures maximum transparency and eases the administration of different environments.